Fujitsu Laboratories Ltd. today announced the development of technology that accelerates transaction processing for Hyperledger Fabric, one of the Hyperledger Blockchain frameworks hosted by The Linux Foundation.
The Blockchain is a technology that creates systems with excellent resistance to falsification while preserving high transparency and reliability, all without centralized management. It is expected to have applications in a variety of fields, particularly in finance.
Now, Fujitsu Laboratories has developed technology to speed up transaction processing by making the processing of communications between applications and the Blockchain platform, which had been the source of bottlenecks, more efficient. In a trial where this technology was implemented in Hyperledger Fabric v0.6.1(1), it increased transaction performance by approximately 2.7 times compared to the previous method.
With this technology, it has become possible to apply Blockchain technology to online transaction systems, which require high performance.
Details of this technology were announced at P2P Financial Systems 2017, an international conference about the Blockchain held in London July 20-21.
Development Background
The Blockchain creates a shared ledger system that, without a centralized manager, is highly transparent and reliable while being extremely difficult to falsify, by requiring the parties involved to mutually verify the accuracy of the transaction data and preserving it in a chain format.
The open source Blockchain framework Hyperledger Fabric, being developed through Hyperledger, in which Fujitsu Limited is a premier member, is the focus of much attention as a Blockchain that is building a robust commercial transaction platform. Hyperledger Fabric uses a consortium-type(2)structure in which the number of participants is limited, and is being trialed for use in a variety of fields, particularly finance, but also for supply-chain management in manufacturing, data conversion of insurance policies, real estate contracts, license management, and energy transactions.
Issues
With Blockchain, groups of nodes based on the number of participants form a network, and work together through the network to perform a series of processes from executing transactions to validating the legitimacy of transactions. For this reason, the number of transactions that can be executed per unit of time is limited by communication bottlenecks through the network, compared to previous centralized systems, making it difficult to apply the technology to things like online transaction systems, which demand high performance, including the ability to immediately process large volumes of transactions.
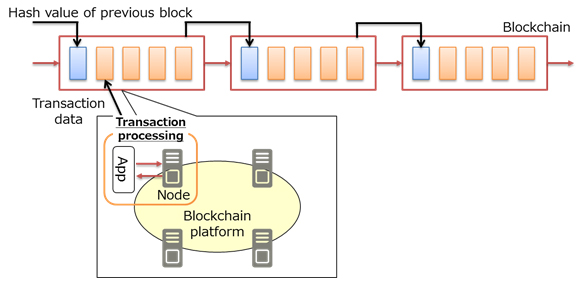 Figure 1: Transaction processing on the Blockchain
Figure 1: Transaction processing on the Blockchain
About the Newly Developed Technology
With the Blockchain, while consensus is formed between participating nodes, transactions are processed by applications reading and writing data on the shared ledger, with safety ensured by linking the transaction data in chain format to be managed.
Using its proprietary analysis technology, Fujitsu Laboratories learned that, under network conditions in which a response time of about 64 milliseconds or less is required, such as the case where a consortium-type Blockchain is operated at multiple locations within Japan, communications between the applications and the Blockchain platform during transaction processing are the primary cause of bottlenecks.
Now, based on these analysis results, Fujitsu Laboratories has developed the following two technologies to improve transaction performance speed by reducing the number of communications between the applications and the Blockchain platform. Features of the newly developed technologies are as follows:
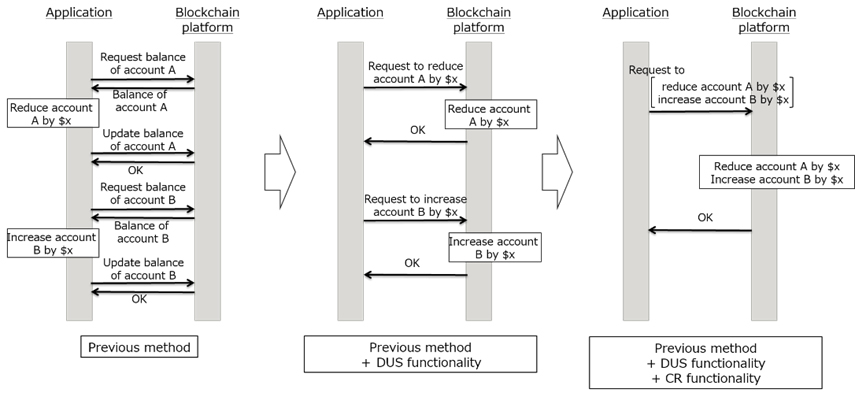
1. Differential Update State (DUS) Functionality
When processing transactions on the Blockchain, a commonly used method is to retrieve the specified data, then handle the computational processing in the application before writing it back to the Blockchain platform. Fujitsu Laboratories has now developed functionality that executes only differential computations on the specified data, in one processing action on the Blockchain platform, and functionality that reduces the number of computations directly linked with the number of communications.
2. Compound Request (CR) Functionality
Fujitsu Laboratories developed functionality to aggregate multiple processes to send to the Blockchain platform for batch execution. This functionality not only makes processing on the Blockchain platform more efficient by aggregating multiple processes, it also reduces the number of communications. The functionality maintains accuracy by rewinding to the origin point of the batch execution if a partial error occurs in the aggregated processes, and reprocessing.
Effects
Fujitsu Laboratories implemented this technology in Hyperledger Fabric v0.6.1 and measured transaction performance on a Blockchain platform consisting of four servers. Whereas the previous method could handle 500 transactions per second, Fujitsu Laboratories achieved 1,350 transactions per second using this newly developed technology, an improvement of approximately 2.7 times.
Future Plans
With this newly developed technology, in terms of performance, the Hyperledger Fabric framework has become applicable to online transaction systems that demand high performance in excess of 1,000 transactions per second, such as those demanded by financial institutions.
Fujitsu Laboratories will continue development of technologies to further speed up the Blockchain while adapting them to the latest version of Hyperledger Fabric, and will carry out trials with a view to commercial applications of this technology, with plans to commercialize it through Fujitsu Limited during fiscal 2017.
-
Stable version of the Hyperledger Fabric framework as of July 5, 2017.
-
Blockchains can largely be divided into three types—public, consortium, and private—of which the consortium-type is regarded as being the strongest contender for applications such as in financial institutions.